
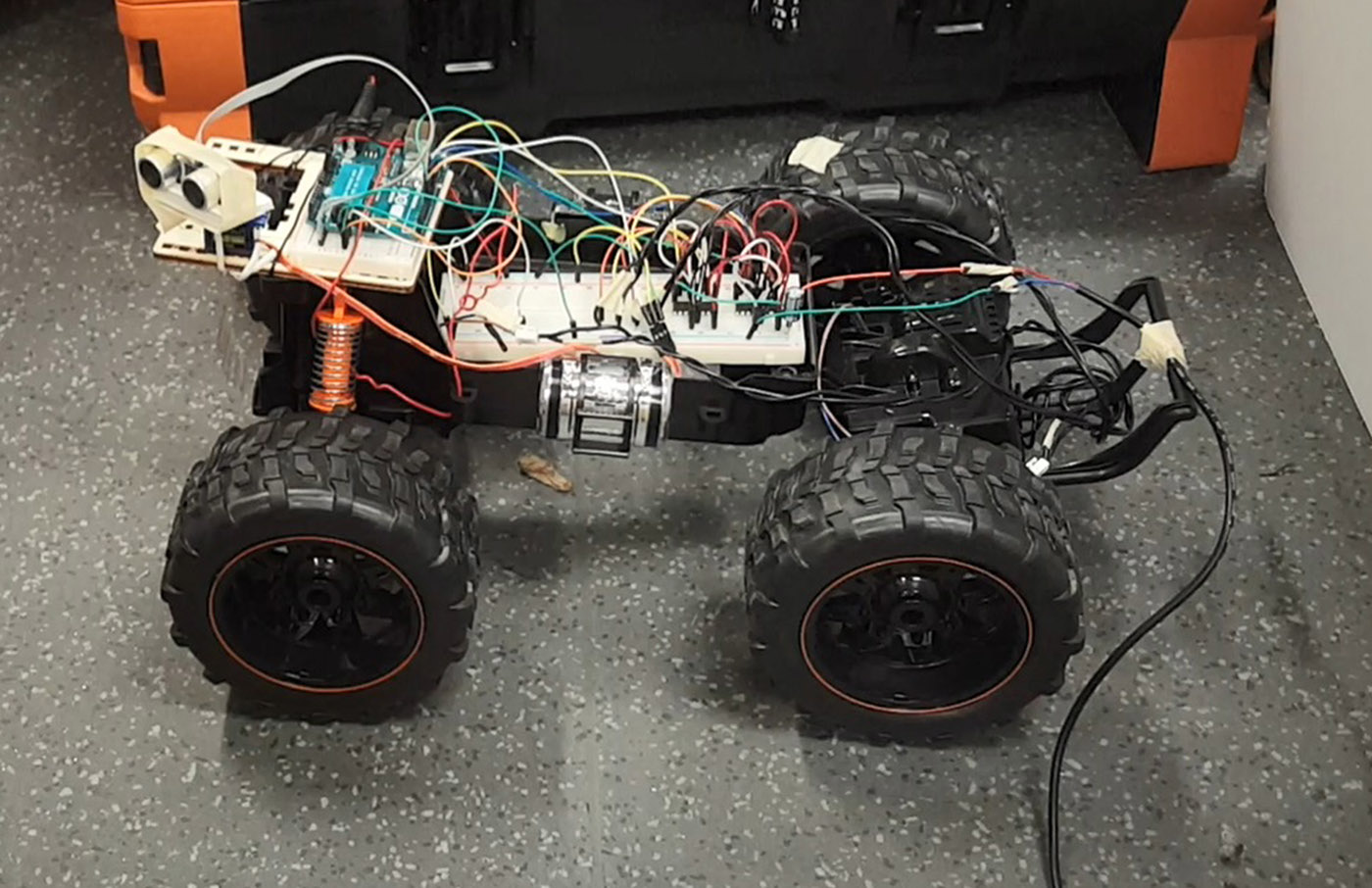



The cable that is connected to the back of the car is the power for 2 dc motors
//The Arduino Group Project
// Hacking an RC car to improve its function by Arduino
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myServo;
long duration, inches, newDistance;
int COLL_DIST = 20;
int LEFT_DIST = 0 ;
int RIGHT_DIST = 0 ;
int LEFT_DIST = 0 ;
int RIGHT_DIST = 0 ;
int trig = 6 ; // attach pin 6 to Trig
int echo = 5 ; // attach pin 5 to Echo
int servoPin = 7 ; // attach pin 7 to Servo
int pos = 0 ;
int curDist = 0 ;
int Case = 0 ;
int echo = 5 ; // attach pin 5 to Echo
int servoPin = 7 ; // attach pin 7 to Servo
int pos = 0 ;
int curDist = 0 ;
int Case = 0 ;
int steering_left = 8 ;
int steering_right = 9 ;
int motor_reverse = 10;
int motor_forward = 11;
//-------------------------------------------------------
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
int steering_right = 9 ;
int motor_reverse = 10;
int motor_forward = 11;
//-------------------------------------------------------
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(motor_forward, OUTPUT) ;
pinMode(motor_reverse, OUTPUT) ;
pinMode(steering_right, OUTPUT);
pinMode(steering_left, OUTPUT) ;
pinMode(motor_reverse, OUTPUT) ;
pinMode(steering_right, OUTPUT);
pinMode(steering_left, OUTPUT) ;
myServo.attach(servoPin);
myServo.write(90);
delay(1000);
myServo.write(144);
delay(1000);
myServo.write(36);
delay(1000);
}
//-------------------------------------------------------
void loop()
{
myServo.write(90);
delay(300);
Case = 0;
distance();
analogWrite(motor_forward, 160); // moving forward
curDist = newDistance;
if (curDist < COLL_DIST)// if the current distance to object is less than the collision distance
{
if (curDist < COLL_DIST)// if the current distance to object is less than the collision distance
{
analogWrite(motor_forward, 0);
delay(1500);
delay(1500);
myServo.write(144);
delay(1000);
distance();
LEFT_DIST = newDistance;
delay(1000);
distance();
LEFT_DIST = newDistance;
// Serial.print(newDistance);
// Serial.print("LEFT ");
// Serial.print("LEFT ");
myServo.write(90);
delay(100);
distance();
curDist = newDistance;
delay(100);
distance();
curDist = newDistance;
myServo.write(36);
delay(1000);
distance();
RIGHT_DIST = newDistance;
// Serial.print(newDistance);
// Serial.print("RIGHT ");
delay(1000);
distance();
RIGHT_DIST = newDistance;
// Serial.print(newDistance);
// Serial.print("RIGHT ");
myServo.write(90);
delay(1000);
delay(1000);
if (RIGHT_DIST > LEFT_DIST) // object is on the left
{
Case = 1;
}
if (RIGHT_DIST < LEFT_DIST) // object is on the right
{
Case = 2;
}
{
Case = 1;
}
if (RIGHT_DIST < LEFT_DIST) // object is on the right
{
Case = 2;
}
}
switch (Case)
{
case 1:
analogWrite(motor_forward, 0);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(steering_left, HIGH); // turn left
//delay(50);
digitalWrite(motor_reverse, HIGH); // backward
delay(500);
digitalWrite(steering_left, LOW);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(motor_reverse, LOW);
delay(500);
switch (Case)
{
case 1:
analogWrite(motor_forward, 0);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(steering_left, HIGH); // turn left
//delay(50);
digitalWrite(motor_reverse, HIGH); // backward
delay(500);
digitalWrite(steering_left, LOW);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(motor_reverse, LOW);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(steering_right, HIGH); //turn right
analogWrite(motor_forward, 160); // forward
delay(700);
analogWrite(motor_forward, 160); // forward
delay(700);
digitalWrite(steering_right, LOW);
delay(500);
analogWrite(motor_forward, 0);
delay(500);
delay(500);
analogWrite(motor_forward, 0);
delay(500);
break;
//---------------------------------
case 2:
//---------------------------------
case 2:
analogWrite(motor_forward, 0);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(steering_right, HIGH); //turn right
digitalWrite(motor_reverse, HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(steering_right, LOW);
delay(500);
analogWrite(motor_reverse, 0);
delay(500);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(steering_right, HIGH); //turn right
digitalWrite(motor_reverse, HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(steering_right, LOW);
delay(500);
analogWrite(motor_reverse, 0);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(steering_left, HIGH); //turn left
analogWrite(motor_forward, 160);
delay(700);
analogWrite(motor_forward, 160);
delay(700);
digitalWrite(steering_left, LOW);
delay(500);
analogWrite(motor_forward, 0);
delay(500);
break;
default:
// if nothing else matches,go forward
analogWrite(motor_forward, 160);
break;
}
delay(500);
analogWrite(motor_forward, 0);
delay(500);
break;
default:
// if nothing else matches,go forward
analogWrite(motor_forward, 160);
break;
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------
void distance()
{
pinMode(trig, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(trig, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trig, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(5);
digitalWrite(trig, LOW);
//---------------------------------------------------
void distance()
{
pinMode(trig, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(trig, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trig, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(5);
digitalWrite(trig, LOW);
pinMode(echo, INPUT);
duration = pulseIn(echo, HIGH);
duration = pulseIn(echo, HIGH);
// convert the time into a distance
newDistance = microsecondsToInches(duration);
// Serial.print(newDistance);
// Serial.println();
newDistance = microsecondsToInches(duration);
// Serial.print(newDistance);
// Serial.println();
delay(100);
}
//-------------------------------------------------
long microsecondsToInches(long microseconds)
{
// According to Parallax's datasheet for the PING))), there are
// 73.746 microseconds per inch (i.e. sound travels at 1130 feet per
// second). This gives the distance travelled by the ping, outbound
// and return, so we divide by 2 to get the distance of the obstacle.
// See: http://www.parallax.com/dl/docs/prod/acc/28015-PI...
return microseconds / 74 / 2;
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------
long microsecondsToInches(long microseconds)
{
// According to Parallax's datasheet for the PING))), there are
// 73.746 microseconds per inch (i.e. sound travels at 1130 feet per
// second). This gives the distance travelled by the ping, outbound
// and return, so we divide by 2 to get the distance of the obstacle.
// See: http://www.parallax.com/dl/docs/prod/acc/28015-PI...
return microseconds / 74 / 2;
}

